Inventory traders have gotten off to a wobbly begin to the brand new 12 months, hobbled by shifting expectations on the timing and extent of Federal Reserve interest-rate cuts in 2024.
All three main U.S. inventory indexes snapped a nine-week profitable streak on Friday, after unexpectedly robust December job beneficial properties prompted merchants to briefly pull again on the possibilities of a March charge lower. The S&P 500
SPX
and Nasdaq Composite
COMP
additionally didn’t stage a Santa Claus Rally from the 5 ultimate buying and selling days of 2023 via the primary two classes of 2024, as questions grew concerning the market’s a number of rate-cuts view.
All of it provides as much as a glimpse of what is perhaps in retailer for traders within the 12 months forward. Already, the so-called “January impact,” or idea that shares are inclined to rise by extra now than every other month, could possibly be put to the take a look at by headwinds that embrace stalling progress on inflation. Inflation’s downward pattern in latest months had given merchants and traders hope that as many as six or seven quarter-percentage-point charge cuts from the Federal Reserve could possibly be delivered in 2024, beginning in March.
Over the primary handful of days within the new 12 months, nevertheless, actuality has began to sink in. For one factor, a number of charge cuts are typically extra generally related to recessions and never comfortable landings for the economic system.
Furthermore, the concept the Fed might observe via with as many charge cuts as envisioned by merchants would considerably enhance the likelihood that policymakers lose their battle in opposition to inflation, in accordance with Mike Sanders, head of fastened earnings at Wisconsin-based Madison Investments, which manages $23 billion in property. That’s as a result of six or extra charge cuts would loosen monetary situations by an excessive amount of, and increase the chance of one other bout of inflation that forces officers to hike once more, he mentioned.
Minutes of the Fed’s Dec. 12-13 assembly present that policymakers have been unsure about their forecasts for charge cuts this 12 months and didn’t rule out the potential of additional charge hikes. Nonetheless, fed funds futures merchants continued to cling to expectations for a giant decline in borrowing prices, with the best probability now coalescing round 5 – 6 quarter-point charge cuts that complete 125 or 150 foundation factors of easing by year-end. That’s roughly twice as a lot as what policymakers penciled in final month, after they voted to maintain rates of interest at a 22-year excessive of 5.25% to five.5%.
Supply: CME FedWatch Instrument, as of Jan. 5.
Uncertainty over the trail of U.S. rates of interest might go away traders flat-footed as soon as once more, and damp the optimism that despatched all three main inventory indexes in 2023 to their finest annual performances of the prior two to a few years. In November, analysts at Deutsche Financial institution AG
DB,
counted seven instances since 2021 wherein markets anticipated the Fed to make a dovish pivot, solely to be improper.
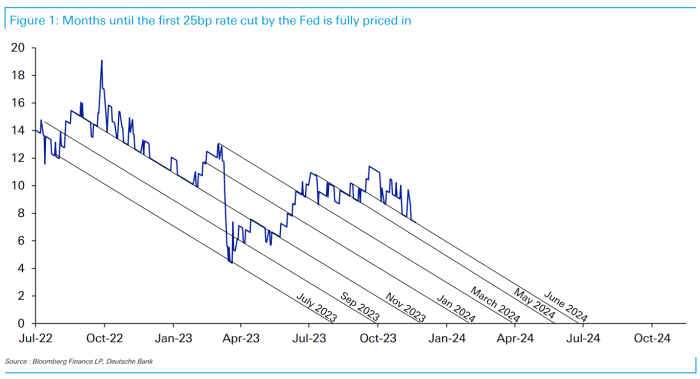
Sources: Bloomberg, Deutsche Financial institution. Chart is as of Nov. 20, 2023.
Monetary markets have been working with “sky-high expectations” for 2024 charge cuts, however the one option to substantiate six cuts this 12 months is with an “abrupt and sharp downturn within the economic system,” mentioned Todd Thompson, managing director and portfolio co-manager at Reams Asset Administration in Indianapolis, which oversees $27 billion.
Heading into 2024, euphoria over the prospect of decrease borrowing prices produced what Thompson calls “an alarming, every little thing rally,” which he says leaves equities and high-yield company debt susceptible to pullbacks between now and the subsequent six months. Past that interval, nevertheless, “the pattern is more likely to be decrease charges because the economic system lastly succumbs to tightening situations on the identical time inflation continues to recede.”
The approaching week brings the subsequent main U.S. inflation replace, with December’s client value index report launched on Thursday. The annual headline charge of inflation from CPI has slowed to three.1% in November from a peak of 9.1% in June 2022. As well as, the core charge from the Fed’s favourite inflation gauge, generally known as the PCE, has eased to 3.2% year-on-year in November from a 4.2% annual charge in July.
The Fed must hold rates of interest greater due to all of the uncertainty round inflation’s most definitely path ahead, and the U.S. labor market “received’t degrade quick sufficient within the first quarter to justify a primary charge lower in March,” in accordance with Sanders of Madison Investments.
Price-cut expectations are “going to be the difficulty for 2024, and plenty of it will be revolving round inflation getting again to that 2% goal,” Sanders mentioned by way of telephone. “We expect someplace between 75 and 125 foundation factors of charge cuts make sense, and that the primary transfer is extra of a June-type of occasion. We don’t assume it is smart to have a March charge lower except the labor market falls off a cliff.”
Historical past reveals that Treasury yields are inclined to fall within the months main as much as the primary charge lower of a Fed easing cycle. Nevertheless, that isn’t occurring proper now. Yields on authorities debt have been on an upward pattern because the finish of December, with 2-
BX:TMUBMUSD02Y,
10-
BX:TMUBMUSD10Y,
and 30-year yields
BX:TMUBMUSD30Y
ending Friday at their highest ranges in additional than two to a few weeks.
See additionally: What historical past says about shares and the bond market forward of a primary Fed charge lower
Whereas monetary markets usually are typically environment friendly processors of data, they “haven’t been very correct by way of pricing in charge cuts” this time, mentioned Lawrence Gillum, the Charlotte, North Carolina-based chief fixed-income strategist for broker-dealer for LPL Monetary. He mentioned the massive danger for 2024 is that if monetary situations ease an excessive amount of and the Fed declares victory on inflation too quickly, which might reignite value pressures in a way paying homage to the Nineteen Seventies interval underneath former Fed Chairman Arthur Burns.
“We expect rate-cut expectations have gone too far too quick, and that the backup in yields we’re seeing proper now could be the market acknowledging that perhaps charge cuts aren’t going to be as aggressive as what was priced in,” Gillum mentioned by way of telephone.
December’s CPI report on Thursday is the info spotlight of the week forward.
On Monday, consumer-credit information for November is about to be launched, adopted the subsequent day by trade-deficit figures for a similar month.
Wednesday brings the wholesale-inventories report for November and remarks by New York Fed President John Williams.
Preliminary weekly jobless claims are launched on Thursday. On Friday, the producer value index for December comes out.

